 Margin trading is a method of trading in the spot market where traders use borrowed funds. To do this, the trader provides their own assets as collateral, which is called margin. By using this system, the trader pays a commission for the use of borrowed funds, calculated based on the interest rate. Margin trading allows users to increase their purchasing power and potential profits from asset price growth, as well as profit from a decrease in cryptocurrency prices. Margin serves as a guarantee for fulfilling obligations to creditors, acting as insurance and acting as an intermediary between the borrower and the lender.
Margin trading is a method of trading in the spot market where traders use borrowed funds. To do this, the trader provides their own assets as collateral, which is called margin. By using this system, the trader pays a commission for the use of borrowed funds, calculated based on the interest rate. Margin trading allows users to increase their purchasing power and potential profits from asset price growth, as well as profit from a decrease in cryptocurrency prices. Margin serves as a guarantee for fulfilling obligations to creditors, acting as insurance and acting as an intermediary between the borrower and the lender.
Leverage
Leverage, also known as leverage, is the ratio between the amount of borrowed funds and the margin. In the cryptocurrency market, the leverage level can range from 2 to 100 times. On cryptocurrency exchanges, the size of leverage is indicated next to trading pairs. For example, for the BTC/USDT pair on the Binance exchange, the leverage is 3x. Thus, if a trader has a deposit of 100 USDT and uses 10x leverage, they can borrow 900 USDT from the broker and open a position worth up to 1000 USDT.
Margin Call and Position Liquidation
Margin call and liquidation (or forced liquidation) are mechanisms used by exchanges to prevent trader debt and losses for creditors. A margin call is a demand from the broker to deposit additional margin into the account to replenish the collateral for open positions. This demand occurs when a trader's margin level falls to a certain risk zone, which is calculated for each trading pair based on market depth and trading volume.
Liquidation refers to the forced closure of a position when its losses almost equal the deposited margin. If the risk level is reached, the trader receives a notification to add more funds. Ignoring this notification and if the price goes down, the exchange will liquidate the position. Alternatively, traders can manually close the position or use a stop-loss order before liquidation, allowing them to preserve part of the margin.
Cross Margin and Isolated Margin
Cross margin and isolated margin are two methods of utilizing margin. With cross margin, all of a trader's funds are used to support all open positions. This means that profits from one trade can offset losses from another. However, if one position incurs significant losses before liquidation, it may result in the liquidation of all open positions.
Isolated margin, on the other hand, allows traders to allocate a specific amount of margin for each individual trade. This way, the liquidation of one position does not affect the other positions.
Index Price in Margin Trading - Definition
The index price is the weighted average price of an asset based on data from multiple markets. Cryptocurrency exchanges use index prices to minimize potential price manipulation. For example, Binance calculates price indices based on data from platforms like Huobi, OKX, Bittrex, HitBTC, Gate.io, BitMEX, MXC, Bitfinex, Coinbase, Bitstamp, Kraken, Binance.US and Bybit.
If the index price goes beyond a certain range during periods of high volatility, exchanges typically warn their customers about the increased risk of position liquidation. In case one of the participating exchanges undergoes maintenance or its price and trading volume data are not functioning, aggregator exchanges temporarily exclude it from calculations. Placing a stop-loss order with the index price as a trigger can help avoid losses due to local market fluctuations on a specific trading platform.
How to Earn Money with Long Margin Trading?
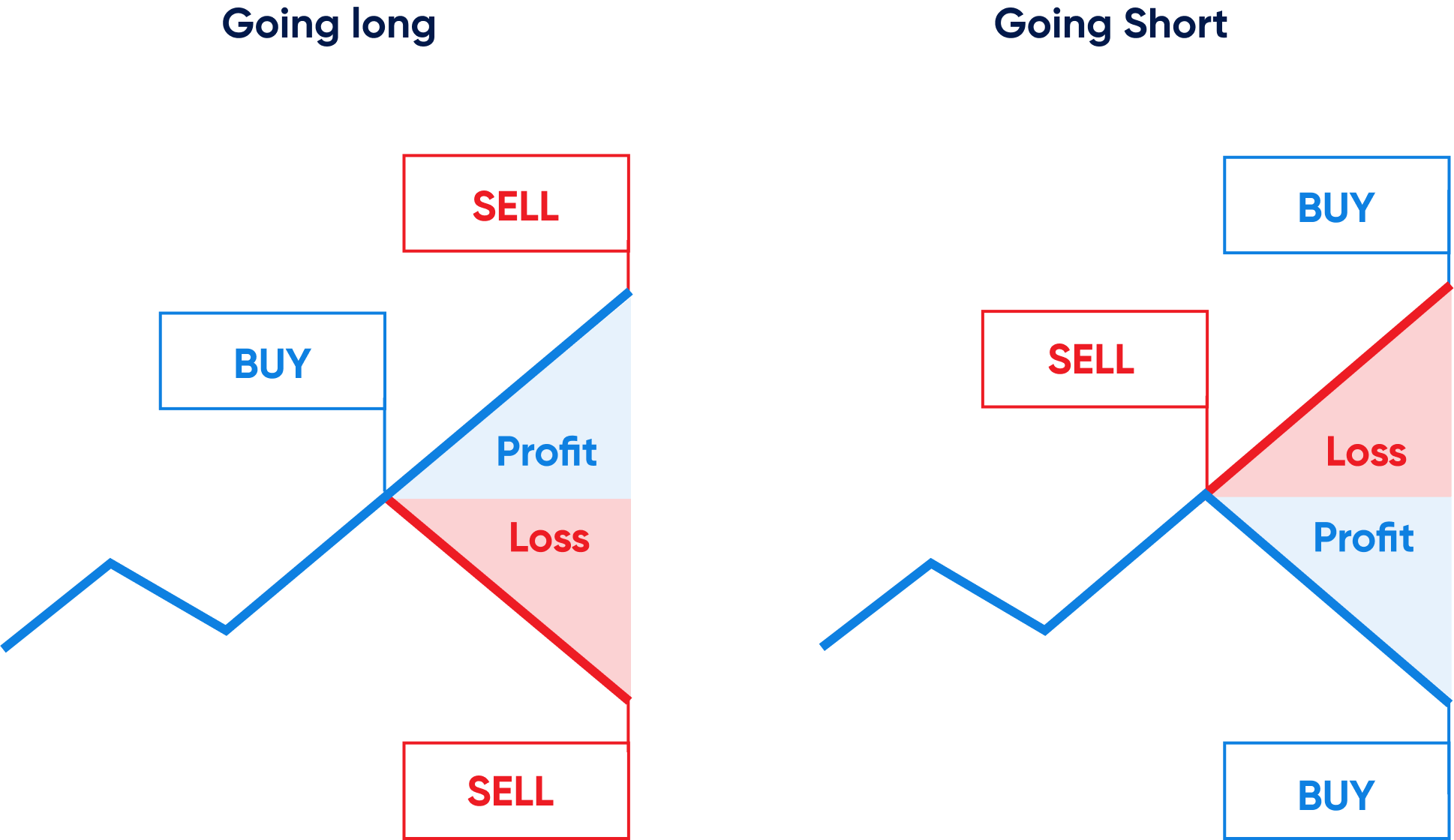
To earn money with long margin trading, a trader buys an asset in anticipation of its price increase. However, to amplify potential profits, leverage can be used. This method allows trading with amounts exceeding the available funds in the account. Let's consider an example of trading Bitcoin on the Binance exchange. Suppose a trader expects the price of Bitcoin to rise from 30,000 USDT to 45,000 USDT. They deposit 10,000 USDT into their margin account and take a 3x leverage loan of 20,000 USDT. The interest rate for using the borrowed funds is 0.013% per day (excluding VIP-level discounts).
Now, the trader can buy Bitcoin for 30,000 USDT. After 10 days, when the asset's price reaches 45,000 USDT, they sell their coins. The net profit from the trade is calculated as follows: Profit from selling 1 BTC (45,000 USDT) - Exchange debt (20,000 USDT) - Broker's fee for using the leverage (26 USDT) - Initial capital (10,000 USDT) = 14,974 USDT. If the trader executed the same trade without using leverage, their profit would be significantly lower: Profit from selling 0.33 BTC (15,000 USDT) - Initial capital (10,000 USDT) = 5,000 USDT. Thus, margin trading with leverage can significantly increase the potential profit for a successful long trade.
How to Earn Money with Short Margin Trading?
To earn money with short margin trading, a trader must sell an asset with the intention to repurchase it at a lower price. It is through margin trading that one can profit from falling asset prices. Let's consider an example of trading Bitcoin on the Binance exchange. Suppose a trader expects the price of Bitcoin to fall from 30,000 USDT to 15,000 USDT. They buy 1 BTC at the current price and take a 5x leverage loan, giving them access to a larger trading amount. The interest rate for the loan is 0.0045% per day (excluding VIP status). Now, the trader sells 5 BTC and receives 150,000 USDT. After 10 days, when the price of Bitcoin falls to 15,000 USDT, they buy back 4 BTC to repay their loan.
The net profit from the trade is calculated as follows: Profit from selling 5 BTC at the price of 30,000 USDT (150,000 USDT) - Purchase of 4 BTC at the price of 15,000 USDT to repay the loan (60,000 USDT) - Initial cost of 1 BTC (30,000 USDT) - Broker's fee for using the leverage (5.4 USDT) = 59,994.6 USDT. Thus, short margin trading allows traders to profit from falling asset prices.
How to Start Trading with Leverage?
To begin trading with leverage, you need to choose a suitable exchange that supports margin trading. Some popular platforms where this is possible include Binance, Huobi, Bitfinex, Kraken, and others. Below are the steps to help you start trading with leverage on the Binance exchange:
-
Register and activate your account on the exchange.
-
Deposit funds into your account that you want to use for leveraged trading.
-
Choose a trading pair available for margin trading and transfer your assets to the corresponding margin account.
-
Decide on your trading direction: long (expecting price increase) or short (expecting price decrease).
-
Wait for a suitable entry point in the market and start using available funds to trade the chosen pair.
-
Manage your positions and control risk. Remember that margin trading involves trading with borrowed funds.
-
Repay your debt to the exchange.
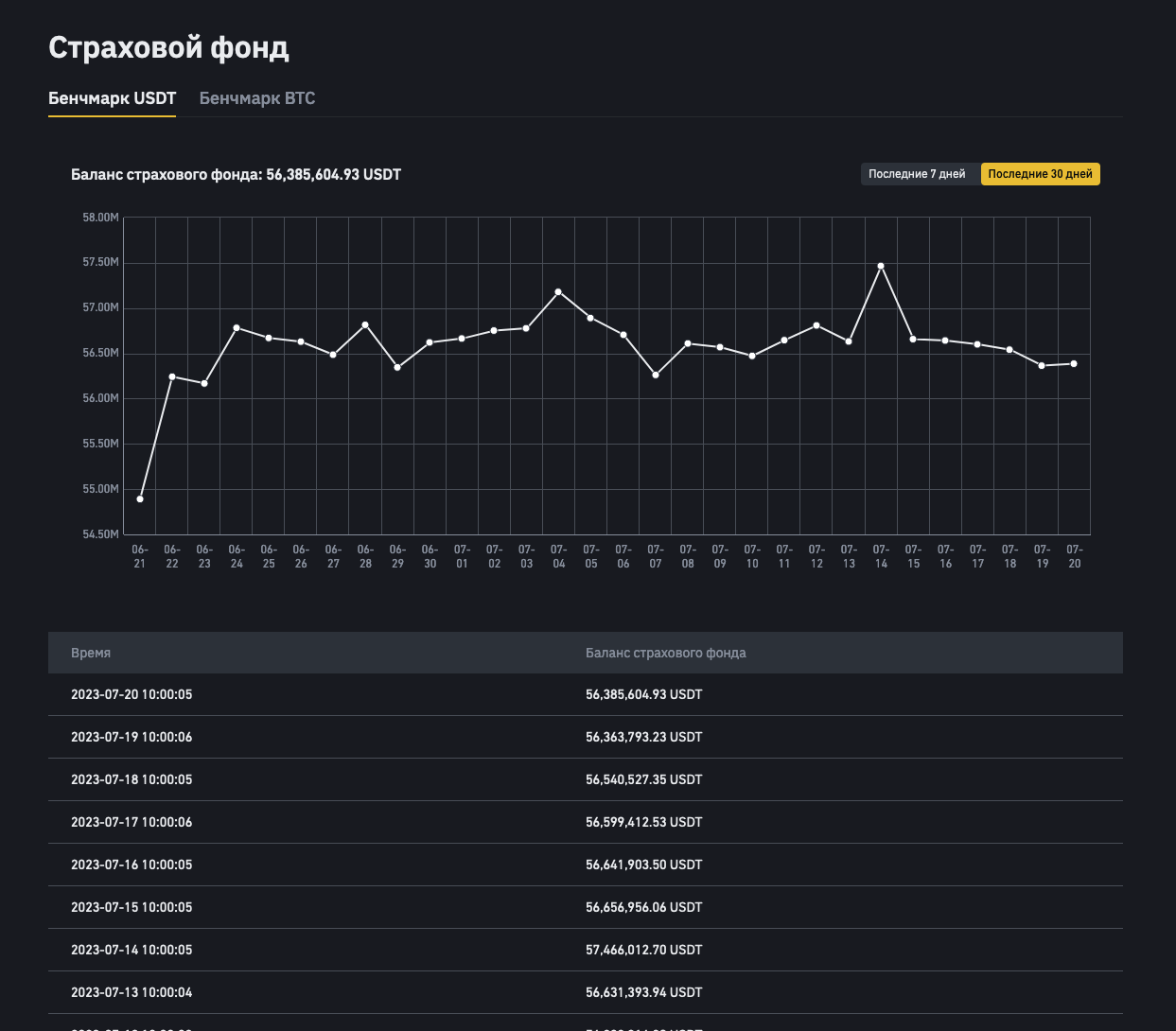
What is a Margin Insurance Fund?
The margin insurance fund is a pool of funds that the exchange allocates to cover potential losses of clients involved in margin trading. For example, on the Binance platform, the margin insurance fund is funded by liquidation fees and revenues from cryptocurrency lending. If a trader's account balance becomes negative after position liquidation, the exchange uses these funds from the insurance fund to compensate the trader's losses.
In case the funds in the margin insurance fund are insufficient at the current moment, Binance provides partial repayment of the debt, but the user won't be able to withdraw funds from the main account until the debt is fully settled. To fully repay the remaining debt, the trader needs to deposit their own funds into the margin account or wait until the insurance fund accumulates enough funds to cover all obligations in chronological order. After the debt is fully repaid, the exchange restores the withdrawal function for the user.
Advantages of Margin Trading with Leverage
Using margin trading with leverage offers several advantages for traders:
-
Access to various markets and assets: Thanks to increased capital in circulation through leverage, traders can participate in different markets and utilize multiple assets simultaneously.
-
Faster achievement of financial goals: Margin trading with leverage allows traders to reach their goals faster compared to similar spot market trading without leverage.
-
Potential unlimited profits: On the cryptocurrency exchange CoinEx, there is no auto-deleveraging as seen in futures markets, meaning the potential profit for traders is not limited.
Risks of Trading with Leverage
However, it is important to note that margin trading with leverage also comes with risks:
-
Total loss of deposit: Losses in leveraged trading can amount to 100% or even exceed the trader's initial deposit.
-
High volatility: During periods of high market volatility, the strategy of margin trading becomes particularly risky.
-
Technical issues: Technical glitches on the trading platform can lead to order execution delays and loss of funds. Therefore, it is essential to choose stable and reliable exchanges for margin trading.