The emergence of smart contracts in cryptocurrencies has propelled the development of decentralized finance (DeFi), but conducting financial operations through smart contracts is only possible within one network (blockchain). For instance, within the Ethereum blockchain, initially, it was only possible to exchange ETH for tokens or NFTs created within that blockchain, thus creating an immediate need for exchanging cryptocurrency and tokens from other blockchains. In other words, initially, it was impossible to exchange Ethereum for Solana or Bitcoin using DeFi. Bridges and wrapped tokens emerged to make such functionality possible. Let's explain what they are.
The emergence of smart contracts in cryptocurrencies has propelled the development of decentralized finance (DeFi), but conducting financial operations through smart contracts is only possible within one network (blockchain). For instance, within the Ethereum blockchain, initially, it was only possible to exchange ETH for tokens or NFTs created within that blockchain, thus creating an immediate need for exchanging cryptocurrency and tokens from other blockchains. In other words, initially, it was impossible to exchange Ethereum for Solana or Bitcoin using DeFi. Bridges and wrapped tokens emerged to make such functionality possible. Let's explain what they are.
A wrapped token is a special smart contract that issues ERC-20 standard tokens on the Ethereum network or any other network supporting smart contracts, pegged to the value of 1 Bitcoin or 1 Solana. They are usually named with the addition of the letter "w" before the cryptocurrency ticker: wBTC, wSOL, wETH, and so forth. For example, currently, through DeFi, you can comfortably buy Bitcoin with Ethereum, but in reality, in this case, you're not purchasing actual Bitcoin but its wrapped copy (Wrapped Bitcoin or wBTC).
Wrapped Bitcoin can only be exchanged back to real Bitcoin on centralized exchanges or through special services like wbtc.network, meaning through intermediaries, as Bitcoin does not support the necessary functionality for smart contracts. In other words, Bitcoin does not support DeFi.
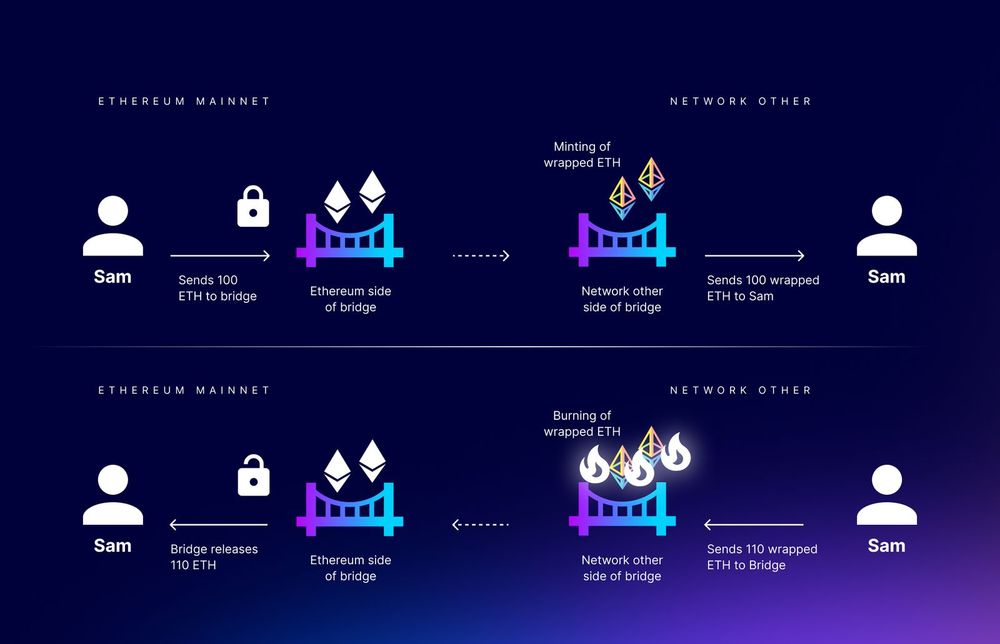
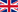
If the exchange occurs between two networks that support smart contracts, for instance, between Ethereum and Binance Smart Chain, the process of exchanging wrapped tokens for real ones in the original blockchain happens automatically through so-called bridges.
The principle of operation of a bridge lies in creating smart contracts in both networks. On one side (on one blockchain), cryptocurrency or tokens can be locked using a smart contract, while, on the smart contract in the second blockchain, an equal amount of wrapped tokens is issued, corresponding to the amount that was locked. In other words, the more cryptocurrency is locked in the main smart contract, the more wrapped tokens are issued in the other smart contract, and vice versa. The number of different bridges and wrapped tokens increases every day as new cryptocurrencies with their independent blockchains emerge, followed by an increase in the number of bridges supporting various token exchange options from one network to another. By connecting cryptocurrencies in this way and thus creating a common blockchain, owning just one ETH or USDT in the ETH network, without resorting to centralized exchanges, using only one's WEB3 wallet, one can buy almost any cryptocurrency through bridges or its wrapped analog in the Ethereum network.
Let's take a closer look at the process of creating and exchanging a wrapped BNB token on the Ethereum network.
Initially, we have two blockchains: Ethereum with the cryptocurrency ETH and Binance Smart Chain with the cryptocurrency BNB.
To introduce the wrapped token wBNB in the Ethereum network, initially, a smart contract is created in the Binance Smart Chain network, which locks the BNB cryptocurrency in its account. In the Ethereum network, in turn, a smart contract is launched that issues ERC-20 standard wrapped tokens called wBNB, and the number of issued tokens will correspond to the amount of BNB that was locked in the original Binance network. The reverse process of unlocking BNB and burning the same amount of wBNB is also possible.
The same process can be repeated in the opposite direction by creating a wrapped token wETH in the Binance Smart Chain network.