 Smart contracts are one of the most transformative innovations brought by blockchain technology. They have revolutionized the automation of transactions, eliminating intermediaries and enhancing transparency and security. But what exactly are smart contracts, how do they function, and why are they so significant in the world of cryptocurrencies? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the fundamentals of smart contracts, their applications, benefits, limitations, and provide practical examples to help you grasp their potential.
Smart contracts are one of the most transformative innovations brought by blockchain technology. They have revolutionized the automation of transactions, eliminating intermediaries and enhancing transparency and security. But what exactly are smart contracts, how do they function, and why are they so significant in the world of cryptocurrencies? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the fundamentals of smart contracts, their applications, benefits, limitations, and provide practical examples to help you grasp their potential.
What Is a Smart Contract?
A smart contract is a self-executing program stored on a blockchain that automatically performs predefined actions when specific conditions are met. In simple terms, it’s a digital agreement that operates on an "if-then" principle: if certain conditions are fulfilled, then the contract executes the specified actions. For instance, if you send cryptocurrency, the smart contract can automatically transfer ownership of a digital asset.
The concept of smart contracts was first introduced by Nick Szabo in 1994, but their practical implementation became possible with the launch of Ethereum in 2015. Ethereum provided a platform where developers could create and deploy smart contracts using the Solidity programming language.
Key Features of Smart Contracts:
- Automation: Smart contracts execute without human intervention, reducing errors and delays.
- Transparency: The contract’s code is stored on the blockchain and is publicly verifiable by all network participants.
- Immutability: Once deployed, a smart contract cannot be altered, ensuring the reliability of its terms.
- No Intermediaries: Smart contracts eliminate the need for third parties, such as banks or notaries.
- Decentralization: Operating on a blockchain, smart contracts are resistant to censorship and system failures.
How Do Smart Contracts Work?
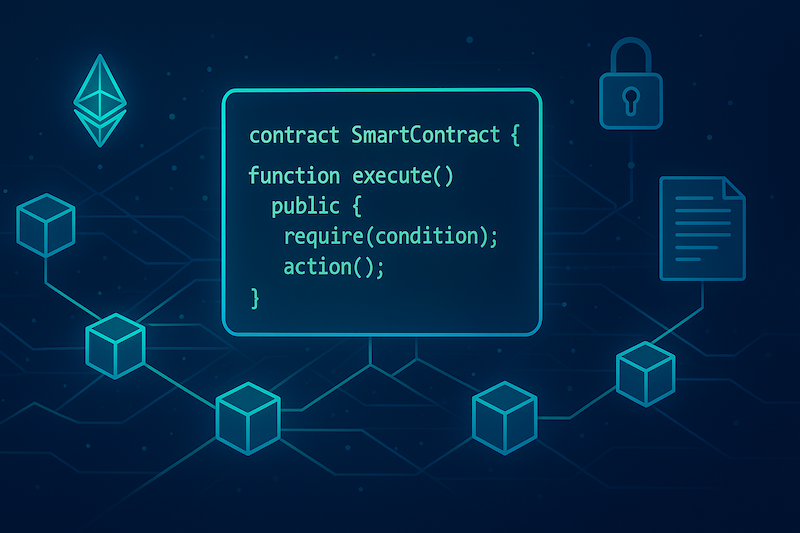
Smart contracts rely on blockchain technology to ensure their security and reliability. Let’s break down their operation step by step:
- Smart Contract Creation: A developer writes the contract’s code in a programming language like Solidity (for Ethereum). The code defines the conditions and actions to be executed. For example, a smart contract for selling a car might state: "If the buyer sends 1 ETH, then ownership is transferred to them."
- Deployment on the Blockchain: Once written, the code is compiled and uploaded to the blockchain, making it public and immutable. Each smart contract is assigned a unique address on the blockchain, which users interact with.
- Condition Verification: When a user interacts with the contract (e.g., sends cryptocurrency or triggers a function), the blockchain verifies whether the specified conditions are met.
- Automatic Execution: If the conditions are satisfied, the smart contract automatically performs the programmed actions, such as transferring tokens, registering ownership, or sending notifications.
- Recording on the Blockchain: All actions performed by the smart contract are recorded on the blockchain, ensuring transparency and irreversibility.
Example of a Smart Contract in Action:
Imagine you want to rent an apartment using a smart contract. The conditions are:
- The tenant sends 0.5 ETH as rent.
- Upon payment, the smart contract automatically provides the tenant with a digital key to access the apartment.
- If no payment is made, the key is not issued.
Here’s a simplified Solidity code example for this scenario:
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.0;
contract RentalAgreement {
address payable public landlord;
uint public rent = 0.5 ether;
bool public isRented;
constructor() {
landlord = payable(msg.sender);
isRented = false;
}
function payRent() public payable {
require(msg.value == rent, "Incorrect rent amount");
require(!isRented, "Apartment already rented");
landlord.transfer(msg.value);
isRented = true;
}
function getKey() public view returns (string memory) {
require(isRented, "Rent not paid");
return "Digital Key: XYZ123";
}
}In this example:
- The tenant sends 0.5 ETH via the payRent function.
- If the amount is correct and the apartment is not rented, the funds are transferred to the landlord, and the status changes to "rented."
- The tenant can call the getKey function to receive the digital key.
Applications of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts are versatile and find applications across various industries. Here are some key use cases:
Finance and DeFi
Smart contracts are the backbone of decentralized finance (DeFi). They enable:
- Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap, where users trade tokens without intermediaries.
- Automated lending and borrowing platforms (e.g., Aave and Compound).
- Management of stablecoins like USDT or DAI, where smart contracts regulate token issuance and burning.
Example: On Uniswap, a smart contract automatically calculates token prices based on liquidity pools, enabling instant asset swaps.

Supply Chain Management
Smart contracts streamline supply chain processes by tracking goods at every stage. For instance, a contract can automatically confirm delivery and release payment to the supplier once the goods reach their destination.
Example: A coffee producer uses a smart contract to track bean shipments from farm to store, logging each step on the blockchain.
NFTs and Digital Art
Smart contracts power the creation, sale, and transfer of non-fungible tokens (NFTs), ensuring ownership and transaction transparency.
Example: An artist creates an NFT artwork, and the smart contract automatically pays them 10% royalties on every subsequent resale.
Voting and Governance
Smart contracts enable transparent and tamper-proof voting systems, preventing fraud as results are recorded on the blockchain.
Example: A decentralized autonomous organization (DAO) uses a smart contract for voting on investment decisions, with each participant’s vote weighted by their token holdings.
Benefits of Smart Contracts
- Time and Cost Efficiency: Eliminating intermediaries reduces fees and speeds up processes.
- Security: Smart contracts are cryptographically secure and operate in a decentralized environment.
- Accuracy: Automation minimizes human errors.
- Transparency: All transactions and conditions are visible on the blockchain.
- Global Accessibility: Smart contracts are accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
Limitations and Risks
Despite their advantages, smart contracts have certain limitations:
- Code Vulnerabilities: Bugs in the code cannot be fixed after deployment. For example, in 2016, hackers exploited a flaw in the DAO smart contract, stealing $50 million.
- Legal Uncertainty: Smart contracts are not always recognized by legal systems, creating regulatory challenges.
- High Gas Fees: On Ethereum, executing smart contracts requires paying "gas" fees, which can be costly during network congestion.
- Limited Flexibility: Smart contracts cannot adapt to changing conditions without deploying a new contract.
The Future of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts continue to evolve. Emerging blockchain platforms like Solana, Cardano, and Polkadot offer faster and cheaper alternatives to Ethereum. Developers are also improving programming languages and tools to create more secure contracts.
In the future, smart contracts could become the foundation for:
- Automated insurance (e.g., payouts for flight delays).
- Digital identity and data management.
- Integration with artificial intelligence for adaptive "smart" contracts.

Conclusion
Smart contracts are a powerful tool transforming industries from finance to logistics. They offer automation, transparency, and security while eliminating intermediaries. However, their use requires caution due to potential code vulnerabilities and legal uncertainties. Understanding how smart contracts work opens up exciting opportunities in the world of cryptocurrencies and blockchain technology.
To dive deeper, consider exploring Solidity and experimenting with smart contracts on Ethereum’s test network. This hands-on approach will help you grasp their mechanics and unlock their full potential.
If you found this material useful, don't forget to subscribe to our Telegram channel.