Revolutionary changes are taking place in the world of financial technologies, altering the familiar rules of the game. Traditional banks and governments have long acted as central controllers, ensuring economic stability. People relied on them to store value and maintain order. However, such a system often led to abuses: high fees, access restrictions, and entry barriers.
Technologies have evolved, and now we can conduct transactions directly, without intermediaries. Decentralized finance, or DeFi, represents an innovative approach where smart contracts on the blockchain replace banks, exchanges, and brokers. This system strives for complete openness, where trust is built on verifiable code rather than blind faith in institutions. Decentralization here does not mean the absence of a center but gives network nodes the freedom of choice.
DeFi combines classic banking services with cryptocurrencies and decentralized applications (DApps), creating a global environment that operates quickly, cheaply, and transparently. This ecosystem breaks down barriers based on status, wealth, and geography. People without bank accounts gain access to transfers, payments, and loans through smartphones. Blockchain protects their digital profiles, allowing even refugees to take out loans and start businesses. DeFi helps combat global poverty by reducing the cost of international transfers through the elimination of intermediaries.
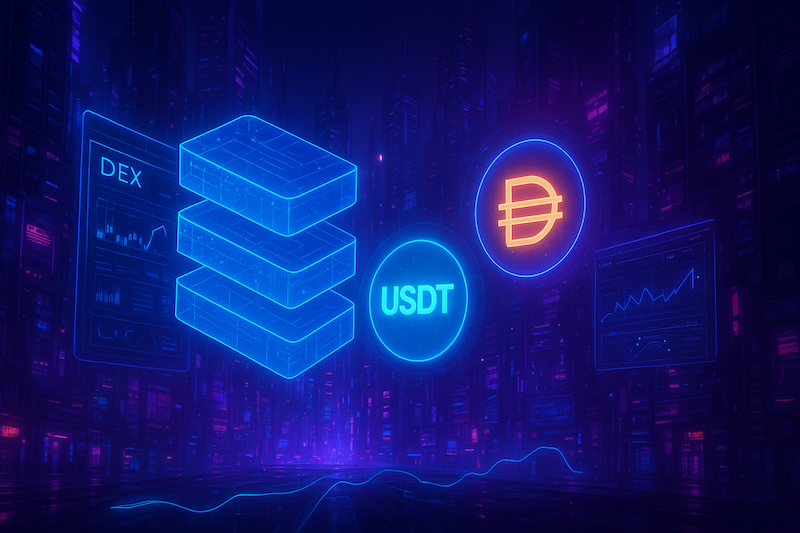
In this article, we will examine the DeFi stack: stablecoins, decentralized exchanges, synthetic assets, money markets, and insurance. These elements demonstrate how blockchain is applied in practice. Cryptocurrencies serve for payments and value storage, while platforms like Ethereum allow programmers to create useful tools. DApps on Ethereum have become the catalyst for DeFi, transforming finance into a transparent and reliable system.
Stablecoins: The Foundation of Stability in DeFi
In the volatile world of cryptocurrencies, stablecoins act as an anchor, holding value steady. They minimize fluctuations by pegging their value to stable assets, such as gold or the US dollar. For example, Tether (USDT) is equivalent to the dollar, making it convenient for storage and transactions.
There are two main types of stablecoins: custodially backed and algorithmic. The first, like USDT, rely on fiat currency reserves in a 1:1 ratio. This ensures that the price does not deviate from the underlying asset. The second use algorithms and smart contracts for stabilization. Instead of real money, cryptocurrencies serve as collateral. DAI on Ethereum is a prime example: the system incentivizes arbitragers through economic mechanisms to keep the price close to the dollar.
Stablecoins bridge the gap between traditional money and crypto. Holders can quickly switch to them to avoid losses from volatility. Reserves always exceed the volume of issued coins, preventing liquidity issues. In DeFi, stablecoins are a key element, providing market calm and allowing focus on investments rather than risks.
Imagine a situation: you hold Bitcoin, but the market is falling. Converting to a stablecoin preserves your value while you wait for recovery. This makes DeFi accessible to newcomers who fear sharp price swings.
Decentralized Exchanges: Trading Without Intermediaries
In traditional markets, exchanges and companies act as intermediaries, charging fees and creating liquidity problems. Often, they operate with insufficient backing, leading to delays. In DeFi, it's different: decentralized exchanges (DEX) allow trading crypto assets directly, without central control.
On platforms like Uniswap, users exchange assets with minimal fees and without the risk of losing control over their funds. Uniswap, launched in 2018, uses an automated market maker (AMM) model, replacing traditional order books.
In AMM, each asset pair forms a separate liquidity pool. Providers add assets proportionally and receive rewards. Trading occurs by swapping one asset for another, with the price determined by the ratio in the pool according to a bonding curve—a convex function where larger orders impact the price more significantly.
This makes trading simple and accessible. There is no need for verification or waiting for approval. You retain full control over your wallet. For traders, this means low costs and high speed, especially compared to centralized platforms.
Consider an example: you want to exchange ETH for USDC. On Uniswap, you connect your wallet, select the pair, and confirm the transaction. Everything happens on the blockchain, without third parties. This model encourages the community to provide liquidity, making the market more resilient.

Synthetic Assets: Mimicking the Real World in DeFi
Synthetic assets are financial instruments that replicate the behavior of other assets. In crypto, they act as derivatives whose value depends on the underlying asset. Options, futures, and swaps give investors flexibility in managing risks and cash flows.
In DeFi, synthetics are essential for liquidity, funding, and market access. Platforms like Synthetix allow creating, trading, and providing liquidity for various assets in a decentralized environment.
How does it work? Users lock collateral (e.g., SNX) to mint synthetic assets. The collateral provides real value. Oracles supply up-to-date prices so the synthetic accurately tracks the target. Traders exchange assets like sUSD, while minters receive SNX rewards for creating liquidity.
This opens doors to investing in stocks, commodities, or currencies without owning them directly. In DeFi, synthetics expand opportunities, allowing risk hedging and portfolio diversification.
Suppose you want to invest in gold but lack access to the physical market. A synthetic on Synthetix provides exposure to gold's price through crypto. This simplifies global trading and lowers barriers.
Money Markets: Lending and Borrowing in DeFi
Liquidity is the heart of any financial system. In the traditional world, banks monopolize lending. In DeFi, money markets allow lending and borrowing crypto assets through protocols, without identification or trust.
Platforms like Compound use liquidity pools: suppliers deposit funds and earn interest, borrowers take loans against collateral with rates depending on supply and demand. No approvals are needed—everything is open and anonymous.
Unlike banks, transparency reigns here: anyone can check loan volumes and ensure the pool is over-collateralized. DeFi offers high yields—sometimes over 10% annually—without credit history, while preserving privacy.
Imagine: you deposit USDT into a pool and earn passively. A borrower uses your funds against ETH collateral, paying interest. If the collateral's price drops, the system automatically liquidates, minimizing risks. This makes lending accessible to everyone, from freelancers to small businesses.
Decentralized Insurance: Protection from Risks in DeFi
DeFi opens financial tools to millions, but risks remain: hacks, like the Poly Network incident, lead to losses. Decentralized insurance covers these threats, protecting deposits, hedging volatility, and safeguarding wallets.
Protocols like Nexus Mutual build a community on smart contracts. Members vote on claims, ensuring fairness. This gives investors confidence, covering losses from exploits or failures.
Insurance in DeFi is not a luxury but a necessity. It lowers entry barriers, making the ecosystem safer. Users pay premiums, and in case of an incident, they receive compensation from the pool. For example, if a platform is hacked, insurance returns the funds. This stimulates DeFi growth, attracting conservative investors.
The Future of DeFi: Transforming Finance
DeFi solves problems of traditional finance: high fees, exclusion, slow transactions, and vulnerabilities. It offers a seamless global experience without borders. Centralized institutions are losing their monopoly. DeFi is accessible to everyone, including the unbanked, and can radically change transactions.
This evolution is full of potential. As technologies grow, DeFi integrates with the real economy, creating hybrid models. However, challenges like regulation and scalability require solutions.
In the end, DeFi is not just a trend but a fundamental shift toward equal opportunities. If you're a newcomer, start small: explore stablecoins, try a DEX. The world of finance is changing, and DeFi is leading this process.