Among all blockchain technologies, Ethereum remains the leader in developing decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. However, the growing popularity of the network leads to issues with throughput, high fees, and delays. This is where zkEVM comes into play - an innovative execution environment that combines the power of zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) with full compatibility with Ethereum. In this article, we will take a detailed look at what zkEVM is, how it works, its key advantages and challenges, as well as future prospects. This guide will help both beginners and experienced users understand why zkEVM is becoming the foundation for the future of Web3.
Among all blockchain technologies, Ethereum remains the leader in developing decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts. However, the growing popularity of the network leads to issues with throughput, high fees, and delays. This is where zkEVM comes into play - an innovative execution environment that combines the power of zero-knowledge proofs (ZKP) with full compatibility with Ethereum. In this article, we will take a detailed look at what zkEVM is, how it works, its key advantages and challenges, as well as future prospects. This guide will help both beginners and experienced users understand why zkEVM is becoming the foundation for the future of Web3.
What is zkEVM and why is it needed?
zkEVM, or Zero-Knowledge Ethereum Virtual Machine, is a virtual machine for executing smart contracts that integrates zero-knowledge proof technology. It is fully compatible with the Ethereum ecosystem, enabling the building of Layer 2 solutions known as ZK-rollups. These rollups are designed to expand the capabilities of the main network by increasing transaction processing speed and reducing gas costs.
Unlike traditional blockchains, where every node must verify all operations, zkEVM uses cryptographic proofs to validate batches of transactions. This makes the network more efficient while maintaining a high level of security. In essence, zkEVM serves as a bridge between the familiar Ethereum world and cutting-edge ZKP technologies, allowing developers to migrate existing projects or create new ones without rewriting code.
Imagine Ethereum as a congested highway: zkEVM adds "express lanes" in the form of L2 solutions, where traffic is processed faster and cheaper, while the main road remains secure.
How zkEVM works: From basics to details
To understand how zkEVM transforms blockchain, let's break down its internal logic step by step. At its core is the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) — the engine that interprets smart contract code written in languages like Solidity and updates the network state after each block.
Execution environment in zkEVM
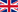
zkEVM emulates the EVM but adds ZKP capabilities. It takes the initial blockchain state, processes a series of transactions, and generates a new state along with a cryptographic proof. This proof confirms that all computations were performed correctly without revealing the details of the operations.
Thanks to this architecture, developers can seamlessly port dApps, tokens, and smart contracts from the Ethereum mainnet to ZK-rollups. No code adaptation is required — everything works just like in the native environment.
Proof generation scheme
Zero-knowledge proofs are a cryptographic tool that allows proving a fact (e.g., having funds in an account) without revealing the data itself. In zkEVM, ZKPs are used to verify transactions: the system creates a "proof" that guarantees the accuracy of the transition from the old network state to the new one.
This is especially useful in scenarios where privacy matters, but computational transparency is required. ZKPs minimize risks and make the system resistant to fraud.
The role of the verifier smart contract
In classic Ethereum, every node verifies transactions individually, which slows down the network. ZK-rollups bundle operations into "batches" and generate a single ZKP for them, which is then sent to the main chain.
A key element here is the verifier smart contract deployed on Ethereum L1. Its operation looks like this:
- Receiving the proof: The contract accepts the ZKP from the rollup.
- State reconciliation: It compares the batch's final data with the initial state.
- Confirmation of the update: If everything is correct, the network state is updated without re-processing the transactions.
Это экономит ресурсы: вместо тысяч проверок достаточно одной верификаци. Безопасность остается на уровне L1, а пропускная способность растет в разы.
Key advantages of zkEVM for users and developers
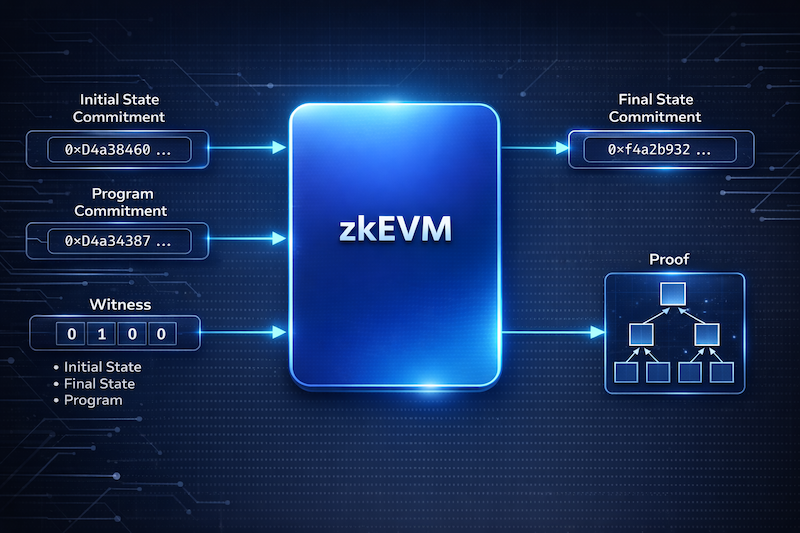
zkEVM offers a number of advantages that make it a preferable alternative to traditional L1 blockchains and other rollups, such as Optimistic Rollups.
Scaling without compromising security
ZK-rollups are not bound by the main network's limitations but inherit its reliability. Transactions are verified through "validation proofs" on L1, allowing optimization of speed without risks. As a result, the network can process thousands of operations per second while preserving decentralization.
Reduced fees
Unlike Optimistic Rollups, where all transaction data is published on L1, zkEVM records only the final state changes. Cryptography has already confirmed correctness, so the data volume is minimal. This directly lowers gas fees, making DeFi and NFTs more accessible to mass users.
Instant transaction finality
Optimistic Rollups require a "challenge period" (1–2 weeks) to dispute operations. In zkEVM, finality occurs immediately after the proof is published. For DeFi traders, this means fast liquidity migration and improved capital efficiency.
Ecosystem effects
Full EVM compatibility provides access to Ethereum's rich infrastructure: tools, libraries, and documentation. The technology has become a standard used in projects like Polygon and Avalanche, strengthening network effects and simplifying integration.
Challenges and pitfalls of zkEVM
Despite the advantages, integrating ZKP and EVM is a complex process. Historically, these technologies developed separately, leading to architectural conflicts.
Stack vs. register architecture
The EVM uses a stack (LIFO), convenient for simple computations but inefficient for ZKP. A register model is better suited for cryptography but requires rebuilding.
Opcode complexity
Specific EVM instructions (CALL, DELEGATECALL) are difficult to adapt to ZK. This complicates verification and slows development.
Data storage
The EVM relies on the Merkle-Patricia tree and Keccak hash, which are not optimized for ZK. Proving their correctness requires massive computations.
Proof resource intensity
Generating ZKPs is computationally expensive and often requires specialized hardware. Early versions, like zkSync Lite, were limited to simple operations.
These issues can be resolved, but they demand innovation from developers.
zkEVM classification: From full compatibility to optimization
Vitalik Buterin classified zkEVMs by the balance between compatibility and proof speed. The closer to Ethereum, the slower the proof generation.
- Type 1: Full Ethereum equivalence. Preserves everything: hashes, trees, consensus. Ideal for native dApps, but proofs take hours (example: Taiko).
- Type 2: EVM equivalence. Optimizes internal mechanisms (replacing Keccak). Application-level compatibility, faster proofs (examples: Scroll, Polygon zkEVM, which transitioned to ZisK in June 2025).
- Type 2.5: With gas adjustments. Increases gas costs for complex operations to speed up proofs, but may require code tweaks.
- Type 3: Near-full compatibility. Excludes rare opcodes to accelerate the network, with partial changes to applications.
- Type 4: Language-level compatibility. Compiles Solidity into a ZK-optimized format. Maximum performance, but addresses and tools differ (examples: zkSync Era, Starknet via Warp).
Projects are evolving: Type 4 is moving closer to Type 2, while Type 2 is optimizing provers.
Future prospects of zkEVM: Toward a global ZK blockchain
zkEVM technology is rapidly evolving. In October 2025, Brevis introduced Pico Prism — a system generating proofs in seconds on gaming GPUs. Average time: 6.9 seconds, with 96.8% of operations in under 10 seconds. This aligns with the Ethereum Foundation's plan for a full ZK transition: an optional zkEVM client for L1, where validators verify three proofs instead of transactions. This would enhance decentralization, allowing stakers to operate on smartphones.
Ryan Sean Adams from Bankless predicts Ethereum will become the global ZK layer for DeFi: "Other chains rely on data centers, Ethereum relies on ZK for scale and decentralization."
Conclusion: zkEVM as the key to scalable Web3
zkEVM is not just a tool — it is the foundation for Ethereum's future. It solves scalability issues while preserving security and compatibility. Despite the challenges, progress in optimization is making it accessible. For investors, developers, and users, this is an opportunity to participate in the evolution of the crypto ecosystem. Keep an eye on updates — zkEVM is changing the rules of the game in blockchain. If you're planning to launch a dApp, start exploring ZK-rollups today!